Contents of Article
- Summary
- What is the 10m Sprint Test?
- Who should use the 10m Sprint Test?
- How do you conduct the 10m Sprint Test?
- What is the scoring system for the 10m Sprint Test?
- What are some considerations for using the 10m Sprint Test?
- Is the 10m Sprint Test valid and reliable?
- References
- About the Author
Summary
The 10m Sprint Test is a simple and popular test used to measure an athlete’s ability to accelerate. As short-distance accelerations are common in a large variety of sports, this test is often included in performance testing batteries. Both handheld stopwatches and electronic timing gates have been proven to be reliable assessment devices. As the distance from the start-line, starting position, and the height of the timing gates have all been shown to affect the test results, it is advised that these are all mandated and kept consistent to avoid testing error.

What is the 10m Sprint Test?
Speed tests are typically used solely to measure an athlete’s linear speed capabilities. More specifically, the 10 metre (m) sprint test is used to measure acceleration. Before the introduction of timing gates, speed tests were typically officiated using stopwatches. While stopwatches are still useful and can be used reliably, the use of timing gates is highly recommended and essential when precision is required (1, 2).
Who should use the 10m Sprint Test?
As the 10m Sprint Test measures acceleration from a static position, it is a common testing protocol as a large majority of sports often involve such short-distance sprint movements. Sports that include any form of short-distance acceleration should often include a 10m sprint test in their performance testing battery.
How do you conduct the 10m Sprint Test?
It is important to understand that whenever fitness testing is performed, it must be done so in a consistent environment (e.g. facility) so it is protected from varying weather types, and with a dependable surface that is not affected by wet or slippery conditions. If the environment is not consistent, the reliability of repeated tests at later dates can be substantially hindered and result in worthless data.
Required Equipment
Before the start of the test, it is important to ensure you have the following items:
- Reliable and consistent testing facility of at least 20m in length (e.g. indoor hall or artificial sports field).
- Test administrators (minimum of two).
- Timing gates x 2 (preferred, but not essential)
- Measuring tape (≥ 10 m)
- Stopwatch
- Marker cones
- Performance recording sheet
Test Configuration
Figure 1 displays the test configuration for the 10m sprint test. This setup must be adhered to if accurate and reliable data is desired.
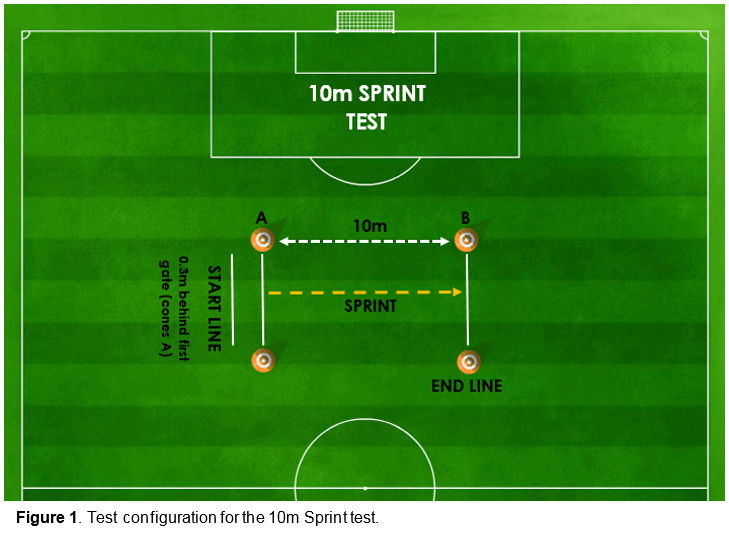
Important information for using timing gates
The distance between the start-line and the first timing gate (cones A – Figure 1) has been shown to affect short-distance sprint times (3). Put simply, the greater the distance, the faster the sprint time as it allows the athlete to generate more speed before crossing the first timing gate. As the 10m sprint is a measure of acceleration, it is recommended the start-line is positioned 0.3m behind the first timing gate in accordance with Altmann et al., (2015) (3).
The height of the timing gates has also been proven to significantly affect the performance results (4). When testing, it is therefore imperative that a standardised, consistent protocol is used to reduce variances within the data. For example, it may be suggested the gates are always set at a consistent height of 1m.
Test Procedure
Warm-up
- Participants should thoroughly warm up prior to the commencement of the test. Warm-ups should correspond to the biomechanical and physiological nature of the test. In addition, sufficient recovery (e.g. 3-5 minutes) should be administered following the warm-up and prior to the commencement of the test.
Starting the test
- Participant readies themselves on the start-line (positioned 0.3 m behind the first gates – cones A) in a standing split-stance start position. NOTE: it is important for reliability that the participant always uses the same starting stance.
- Participant should be counted down ‘3 – 2 – 1 – GO ‘.
- If the test administrators are using a stopwatch, then the timekeeper must stand at the finish line and perform the countdown and time the sprint.
- On the ‘GO’ signal, the participant must accelerate maximally to the finish line as quickly as possible.
- Each participant MUST complete a MINIMUM OF THREE SPRINTS, each separated by a 2-3 minute rest if reliable results are desired.
After the test
- Once the test is over, some subjects may react to the previous exertion. To reduce any problems, the subjects should rest, either sitting or standing, for at least 2-3 minutes. If the subject feels ill or goes quiet or pale, they should lie down with their feet resting on a chair. Note: never leave the participant alone after the test.
What is the scoring system for the 10m Sprint Test?
If three sprints are completed, all the scores are normally then generated into a mean score which provides an overall 10m sprint time. This is done by using the following equation:
- Mean score (seconds) = (#1 sprint time + #2 sprint time + #3 sprint time) ÷ total number of sprints (e.g. 3)
What are some considerations for using the 10m Sprint Test?
When conducting the test, there are several factors that need to be taken into consideration before you begin – some being:
- Accuracy of the stopwatch – Though hand-held stopwatches have been proven to be reliable when measuring speed, they are not recommended when high degrees of precision are required (1, 2). If timing gates are not available, then it is imperative the test administrators understand the inconsistencies of using a stopwatch for their results. As a result, test administrators must pay great attention and attempt to communicate clearly in order to maximise the accuracy of the results.
- Starting stance – As the starting position can impact performance (5), it is suggested participants always adopt the same starting position. The split stance (one leg forward, and one back) is most recommended.
- Starting distance from first timing gate – As previously discussed, the distance between the start line and the first set of gates significantly affects sprint times. Therefore, it is essential to remain consistent with the set-up configuration. For the 5m Sprint Test, we recommended a distance of 0.3m.
- The height of the timing gates – To the author’s knowledge, only one study to date has assessed the effects of timing gate height on sprint performance (4). The authors measured significant sprint time differences when the gates were set at 60cm and 80cm. However, there is no current research that identifies an optimal height for testing. As a result, it is highly recommended test administrators adopt one height (e.g. 1m) and stick to it.
- Circadian rhythms – Circadian rhythms have been shown to significantly alter anaerobic performance tests. Current knowledge suggests that early morning anaerobic tests will elicit significantly lower peak power values than late afternoon or evening tests (6).
- Surface and Conditions – Before conducting the test, ensure the surface is non-slip and consistent (e.g. not affected by weather). Secondly, ensure the environment/ facility is also consistent and not affected by weather conditions.
- Individual effort – Sub-maximal efforts can result in inaccurate and meaningless scores.
Is the 10m Sprint Test valid and reliable?
Numerous research has confirmed the validity and reliability of the 10m Sprint Test using electronic timing gates (4, 7, 8). Whilst no research, in particular, verifies the reliability of using hand-held stopwatches for the 10m Sprint Test, other research has concluded the reliability of stopwatches on similar short-distance sprints (1, 2).
- Hetzler, RK, Stickley, CD, Lundquist, KM, and Kimura, IF. Reliability and accuracy of handheld stopwatches compared with electronic timing in measuring sprint performance. J Strength Cond Res 22(6): 1969–1976, 2008 [PubMed]
- Mayhew, JL, Houser, JJ, Briney, BB, Williams, TB, Piper, FC, and Brechue, WF. Comparison between hand and electronic timing of 40-yd dash performance in college football players. J Strength Cond Res 24(2): 447–451, 2010 [PubMed]
- Altmann, S, Hoffmann, M, Kurz, G, Neumann, R, Woll, A, and Haertel, S. Different starting distances affect 5-m sprint times. J Strength Cond Res 29(8): 2361–2366, 2015 [PubMed]
- Cronin, J.B., & Templeton, R.L. (2008). Timing light height affects sprint times. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 22(1), 318-320. [PubMed]
- Cronin, J.B., J.P. Green, G.T, Levin, M.E. Brughelli, and D.M. Frost. Effect of starting stance on initial spring performance. Strength Cond. Res. 21(3):990–992. 2007. [PubMed]
- Teo, W., Newton, M.J., & McGuigan, M.R. (2011). Circadian rhythms in exercise performance: Implications for hormonal and muscular adaptation. Journal of Sports Science and Medicine, 10, 600-606. [PubMed]
- Duthie, G.M., D.B. Pyne, A.A. Ross, S.G. Livingstone, and S.L. Hooper. The reliability of ten-meter sprint time using different starting techniques. Strength Cond. Res. 20(2)246:–251. 2006. [PubMed]
- Marques, MC and Izquierdo, M. Kinetic and kinematic associations between vertical jump performance and 10-m sprint time. J Strength Cond Res 28(8): 2366–2371, 2014 [PubMed]




